TM 55-203
open by a spring-loaded diaphragm.
As pressure
contained in a specially constructed heated car carried at
increases in these chambers, a piston is moved, which
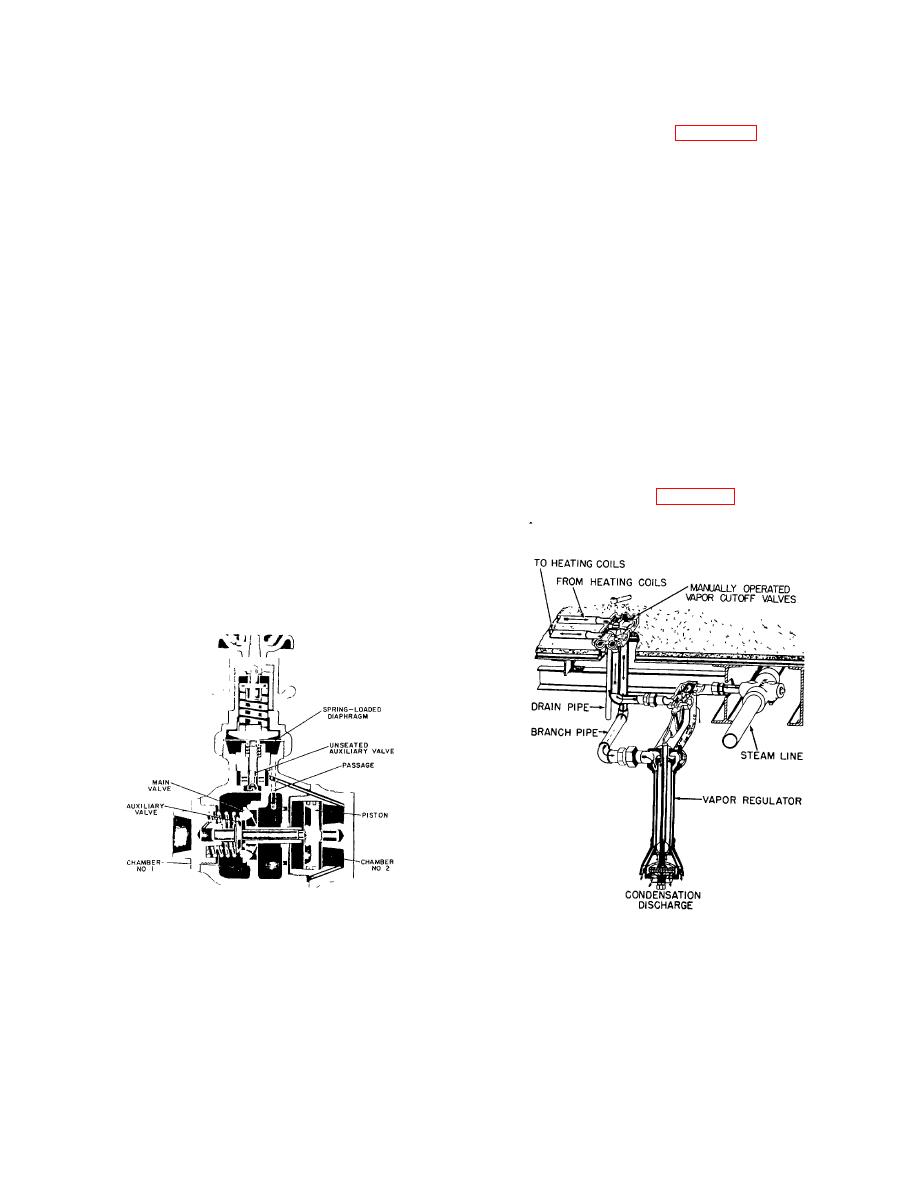
the head end of the train. In figure 11-3, a vapor system
forces open an auxiliary and a main valve in the pressure-
for one side of a passenger car is shown provided with
reducing valve Steam under pressure is permitted to
manual controls. An identical system is employed on the
move upward and exert pressure on the spring-loaded
other side of the car. The system consists of a ,steam
diaphragm The auxiliary valve is then closed. As the
line underneath the car; a vapor regulator, -also on the
steam condenses and pressure is reduced, the spring
underside of the car; and two vapor ,cutout valves from
again exerts tension on the auxiliary valve and opens it,
which heating coils of the car are supplied. The vapor
simultaneously opening and closing valves and ports as
regulator is connected to the steam line by a branch pipe
required. The spring on the springloaded diaphragm can
in which a constant-pressure valve and a standard cutoff
be adjusted to exert any desired pressure.
valve are installed.
11-4. Steam Vapor System
11-5. Vapor Zone System
Steam at atmospheric pressure is termed vapor. At sea
a. Compared to the manual system, the vapor
level, its temperature is 212 . In theory, when steam
F
zone system gives a better distribution of heat and a more
condenses to water it gives off the same amount of heat
uniform temperature through the car and makes more
that was required to convert the water to steam.
economical use of steam. In this system the car is
Therefore, the maximum quantity of heat is recoverable
divided into two or more zones or areas, each of which is
when vapor at 212 . condenses to water at that
F
fitted with a separate radiation system and a flow-limit
temperature, imposing the least drain on the boiler or heat
valve under independent thermostatic control. Radiation,
source. The vapor system, like all other steamheat
usually of the fin-tube type, may be located either on the
systems, obtains steam or vapor from the locomotive or
floor or overhead. A one-zone diagram of this type of
from a flash boiler. Delivery is controlled by a pressure
heating system is shown in figure 11-4.
regulator. The regulator is controlled manually in the
locomotive by opening and closing cutout valves which
regulate the amount of steam entering the car radiator
system. The regulator generally is set to deliver steam at
approximately 15 pounds pressure per car in the train. In
diesel operations, the source of steam sometimes is
Figure 11-3. Hand-operated vapor system.
Figure 11-2. Pressure-reducing valve.
11-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
