3.15.
SIZE
Recent trends in track construction have been toward larger and higher quality ties, not
only for more effectiveness in service but for economic reasons as well. For the rails to have
satisfactory support, a tie should approach 9 inches in width. Standard tie length in the United
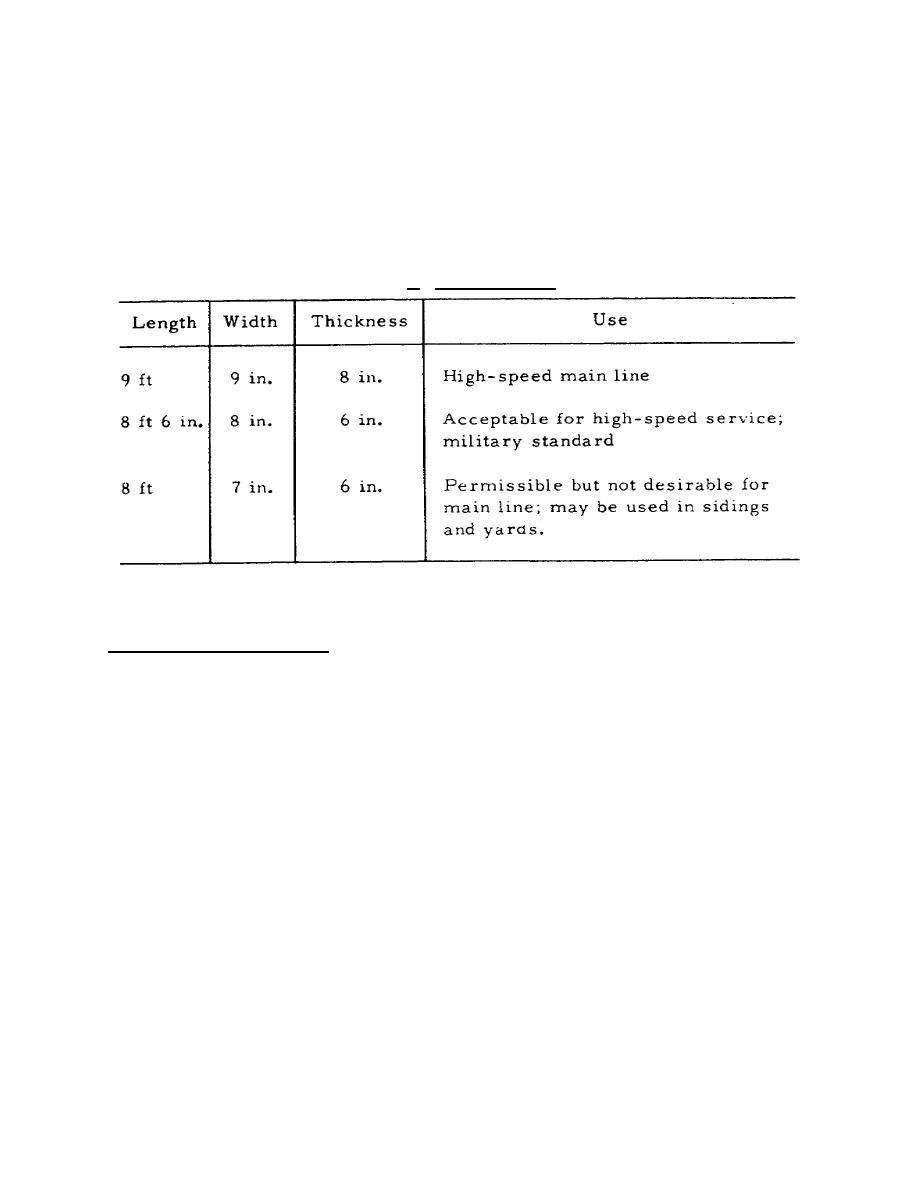
States varies from 8 to 9 feet; tie thickness, from 6 to 7 inches. Given in table II are typical tie
sizes with recommended uses for each.
Table II. Typical Tie Sizes
Bridge ties are sized and spaced to conform with the design of the particular bridge. Ties
placed under switches are longer than standard ones. Switch tie size is discussed further in
Railway Track Maintenance II.
3.16.
SPACING
The number of ties per length of track depends on the volume, weight, and speed of the
traffic and on rail weight. The decision as to the number of ties per rail length depends upon
the space to be left between them, the length of unsupported rail. Experience shows that this
space should not exceed 18 inches. For case in manual tamping, the space should not be less
than 10 inches; for machine tamping, 8 inches is sufficient. On tangents, military engineers
prescribe spacing ties at 24-inch intervals, measured from the center of one tie to the center of
the next one; on curves and through tunnels, at 22-inch intervals.
One large commercial railroad specifies the spacing for ties given in table II.
52



 Previous Page
Previous Page
